Transforming Waste Into Value: The Rise Of Products From Recycled Materials
Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials
Related Articles: Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials
- 3.1 A Paradigm Shift: From Waste to Resources
- 3.2 A Spectrum of Innovation: Products from Waste Materials
- 3.3 Benefits of Products from Recycled Materials
- 3.4 Challenges and Opportunities
- 3.5 FAQs about Products from Waste Materials
- 3.6 Tips for Choosing Products from Recycled Materials
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Through Waste Transformation
- 4 Closure
Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials

The world is increasingly grappling with the consequences of its consumption habits. Mountains of discarded materials, ranging from plastic bottles to electronic waste, threaten our environment and deplete precious resources. However, amidst this crisis, a revolution is brewing: the transformation of waste into valuable products. This shift, driven by innovation and environmental awareness, is not only reducing waste but also creating a new generation of sustainable and economically viable products.
A Paradigm Shift: From Waste to Resources
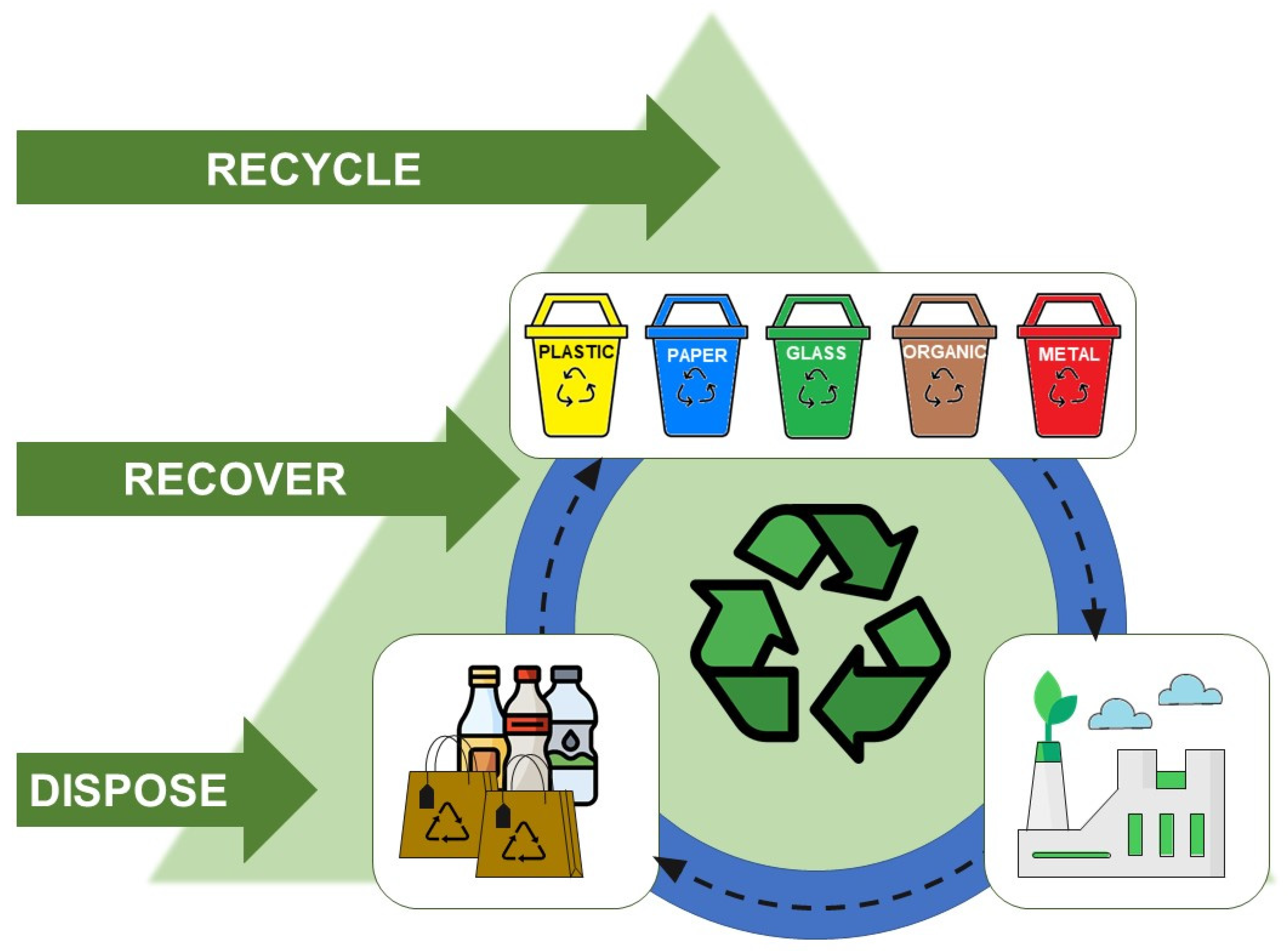
The traditional linear model of "take, make, dispose" has proven unsustainable. It relies on the extraction of finite resources, leading to environmental degradation and resource depletion. The circular economy, in contrast, embraces a closed-loop system where materials are kept in use for as long as possible. This principle involves minimizing waste generation, reusing and recycling materials, and ultimately closing the loop by creating new products from recycled materials.
This transition is driven by a confluence of factors. Growing environmental concerns, coupled with stricter regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products, are pushing businesses to adopt circular practices. Technological advancements have also played a crucial role, enabling the efficient processing and transformation of waste materials into high-quality products.
A Spectrum of Innovation: Products from Waste Materials
The range of products derived from recycled materials is vast and constantly expanding. Here are some prominent examples:
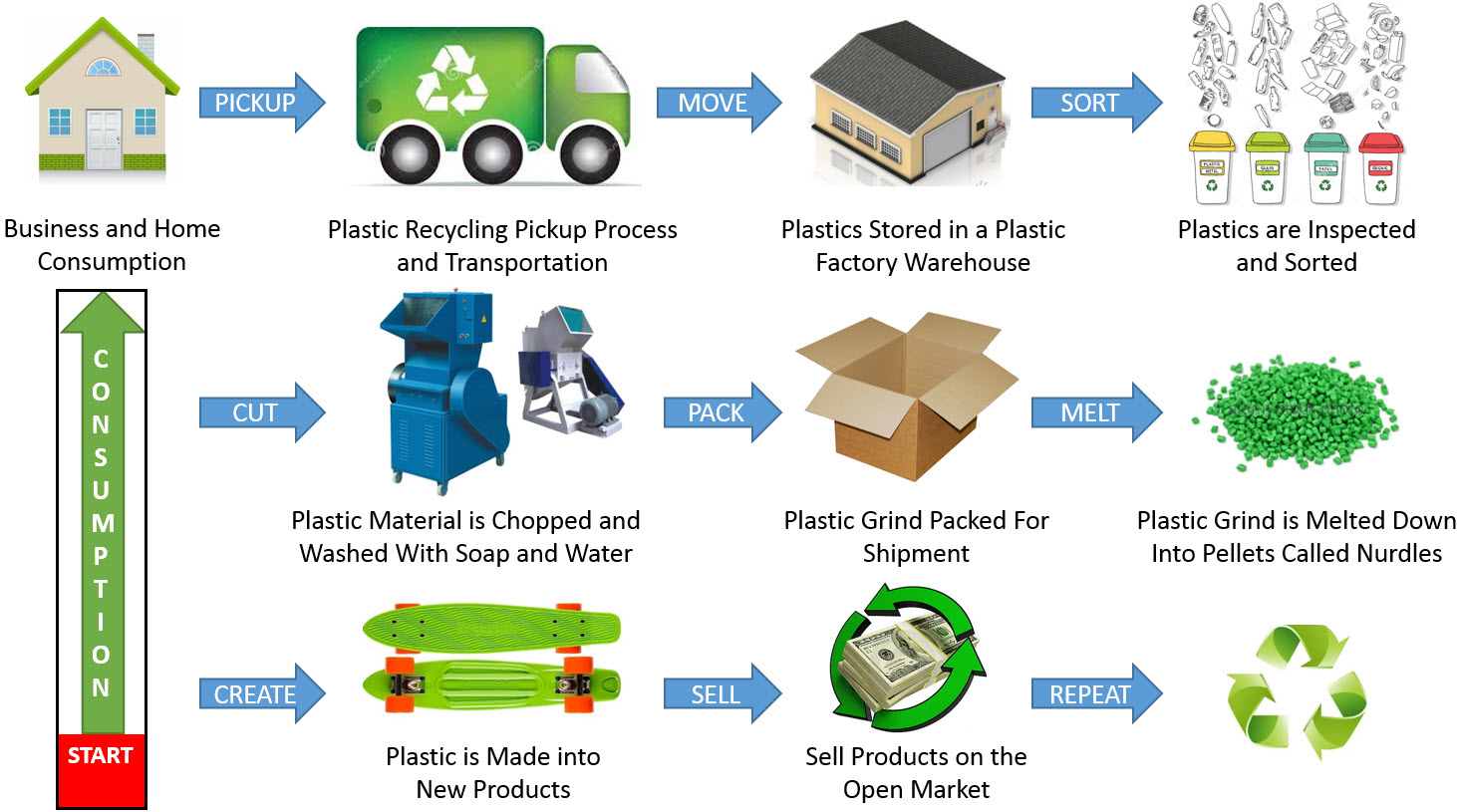
1. Plastics: A Second Life for Discarded Bottles and Packaging
- Textiles: Recycled plastic fibers are used to create clothing, carpets, and upholstery, reducing the reliance on virgin materials and minimizing textile waste.
- Building Materials: Plastic waste is incorporated into composite materials for construction applications, such as decking, fencing, and roofing.
- Packaging: Recycled plastic can be used to manufacture new packaging materials, reducing the need for virgin plastic and promoting a circular economy within the packaging industry.
2. Paper: Transforming Paper Waste into New Products
- Paperboard: Recycled paper is processed into paperboard, which is used for packaging, cartons, and other applications.
- Insulation: Recycled paper fibers can be used to create insulation for buildings, reducing reliance on energy-intensive materials and improving energy efficiency.
- Compost: Paper waste can be composted to create a nutrient-rich soil amendment, reducing landfill waste and promoting sustainable gardening practices.
3. Glass: From Bottles to New Products
- Glass Cullet: Crushed glass, known as cullet, is used as a raw material in the production of new glass products, reducing the energy required for glass manufacturing.
- Sandblasting Media: Recycled glass can be used as abrasive media for sandblasting, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional sandblasting materials.
- Decorative Elements: Recycled glass can be transformed into decorative items such as tiles, mosaics, and art pieces, adding a unique and sustainable touch to interior design.
4. Metals: Recovering Valuable Materials from Scrap
- Aluminum: Recycled aluminum is used in the production of cans, foil, and other products, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to using virgin aluminum.
- Steel: Scrap steel is melted and reformed into new steel products, ensuring the continued use of valuable metal resources.
- Copper: Recycled copper is used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and other applications, offering a sustainable alternative to mining new copper.
5. Electronic Waste: Recovering Valuable Metals and Components
- Precious Metals: E-waste contains valuable metals like gold, silver, and platinum, which can be recovered and used in new electronics and other industries.
- Components: Components from discarded electronics, such as circuit boards, can be reused or refurbished for new devices.
- Materials for Construction: Some components of e-waste, such as plastic casings and metal parts, can be recycled for use in construction materials.
Benefits of Products from Recycled Materials
The transition to products made from recycled materials offers a myriad of benefits:
- Environmental Protection: Reducing reliance on virgin materials minimizes the extraction of natural resources, thereby protecting ecosystems and reducing pollution.
- Resource Conservation: Recycling and reuse extend the lifespan of materials, reducing the need for new materials and mitigating resource depletion.
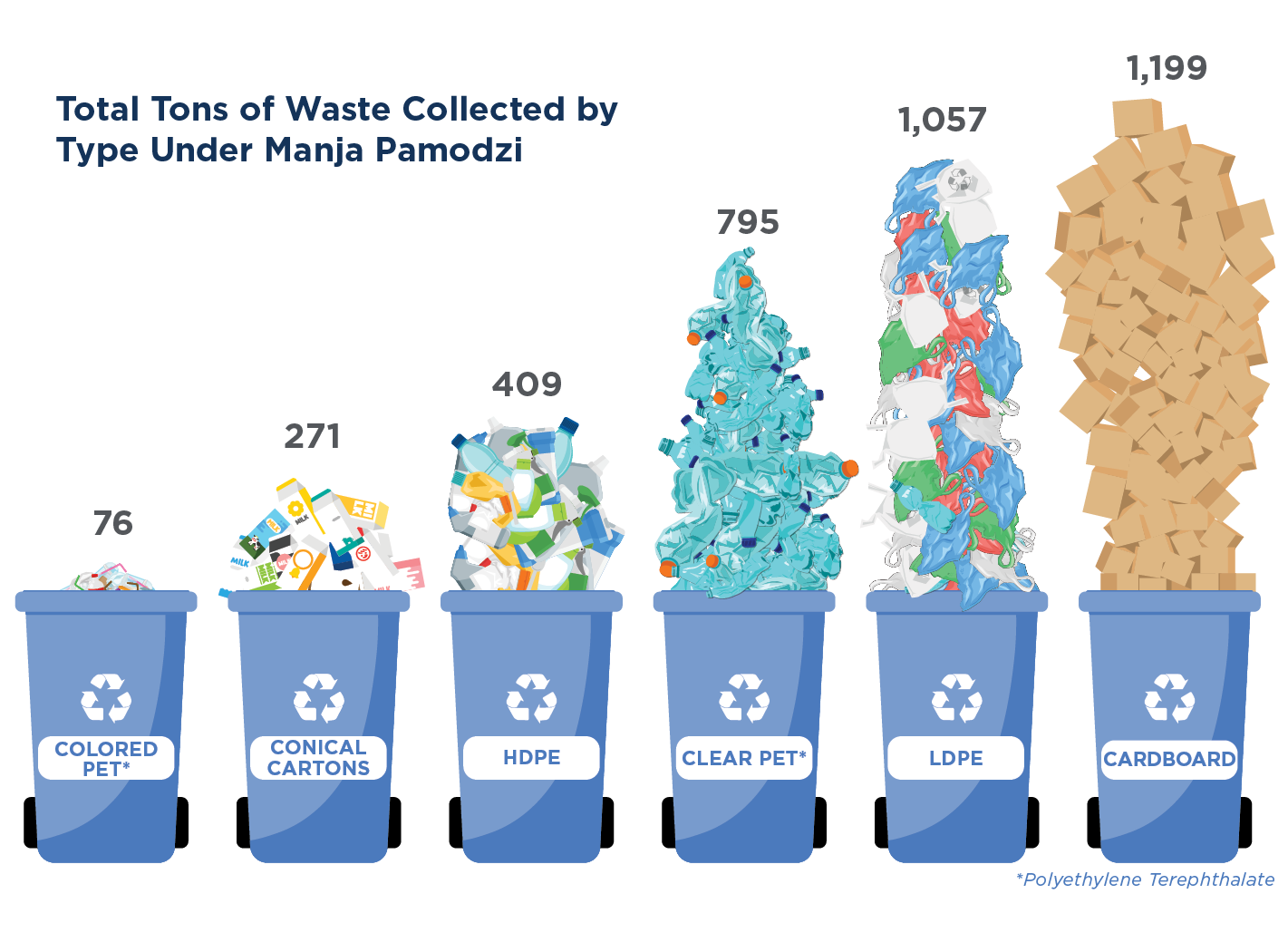
- Waste Reduction: Recycling and upcycling waste materials significantly reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Energy Savings: Manufacturing products from recycled materials typically requires less energy than producing them from virgin materials, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and energy dependence.
- Economic Growth: The recycling and upcycling industries create new jobs and stimulate economic growth, fostering innovation and sustainability.
- Social Impact: Utilizing recycled materials promotes social responsibility and encourages a shift towards a more sustainable and equitable society.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the numerous benefits, the widespread adoption of products from recycled materials faces several challenges:
- Cost and Infrastructure: Recycling and upcycling processes can be costly, requiring investments in infrastructure, technology, and skilled labor.
- Market Demand and Consumer Perception: Consumer awareness and demand for recycled products remain a significant factor in driving market adoption.
- Quality and Consistency: Ensuring the quality and consistency of recycled materials is crucial for their successful integration into manufacturing processes.
- Regulation and Policy: Effective policies and regulations are essential to incentivize recycling and create a level playing field for companies using recycled materials.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Technological advancements, such as advanced sorting and recycling technologies, are continuously improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of recycling processes. Growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products are creating a market pull for recycled materials. Governments and businesses are increasingly recognizing the need for a circular economy and are implementing policies and programs to support the transition.
FAQs about Products from Waste Materials
1. What are the most common products made from recycled materials?
The most common products made from recycled materials include packaging, textiles, building materials, paper products, and aluminum cans.
2. How does recycling contribute to sustainability?
Recycling conserves natural resources, reduces landfill waste, and minimizes pollution. It also reduces the energy required to manufacture new products from virgin materials.
3. What are the challenges of using recycled materials?
Challenges include the cost of recycling, the need for advanced technology, and ensuring the quality and consistency of recycled materials.
4. What are some examples of innovative products made from recycled materials?
Examples include recycled plastic furniture, building materials made from recycled glass, and clothing made from recycled plastic bottles.
5. How can I support the use of recycled materials?
Support local recycling programs, choose products made from recycled materials, and advocate for policies that promote sustainability.
Tips for Choosing Products from Recycled Materials
- Look for the Recycling Symbol: The recycling symbol on packaging indicates that the product contains recycled materials.
- Check Product Labels: Look for labels that specify the percentage of recycled content in the product.
- Support Companies with Sustainable Practices: Choose companies that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing waste.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about the benefits of recycling and share your knowledge with friends, family, and colleagues.
- Advocate for Change: Support policies and initiatives that promote recycling and the use of recycled materials.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Through Waste Transformation
The transformation of waste into valuable products represents a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. By embracing circular economy principles, we can reduce our reliance on virgin materials, minimize environmental impact, and create a more resilient and equitable society. Through innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainable practices, we can unlock the potential of waste materials and build a world where waste is not discarded but transformed into valuable resources.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Waste into Value: The Rise of Products from Recycled Materials. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!